Digital Map Of Bangladesh
Digital Map Of Bangladesh' title='Digital Map Of Bangladesh' />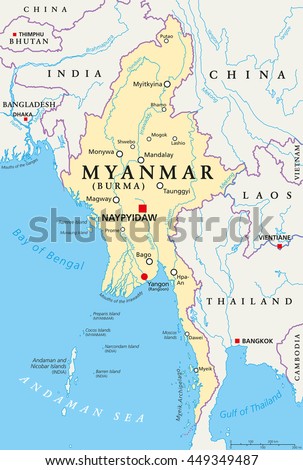

.jpg) DVB T Wikipedia. DVB T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting Terrestrial it is the DVB European based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1. UK in 1. 99. 8. 1 This system transmits compresseddigital audio, digital video and other data in an MPEG transport stream, using coded orthogonal frequency division multiplexing COFDM or OFDM modulation. It is also the format widely used worldwide including North America for Electronic News Gathering for transmission of video and audio from a mobile newsgathering vehicle to a central receive point. Rather than carrying one data carrier on a single radio frequency RF channel, COFDM works by splitting the digital data stream into a large number of slower digital streams, each of which digitally modulates a set of closely spaced adjacent sub carrier frequencies. In the case of DVB T, there are two choices for the number of carriers known as 2. K mode or 8. K mode. These are actually 1,7. Hz or 1 k. Hz apart. DVB T offers three different modulation schemes QPSK, 1. QAM, 6. 4QAM. DVB T has been adopted or proposed for digital television broadcasting by many countries see map, using mainly VHF 7 MHz and UHF 8 MHz channels whereas Taiwan, Colombia, Panama and Trinidad and Tobago use 6 MHz channels. Examples include the UKs Freeview. Map of India and Bangladesh showing the geographical location of Bangladesh and India along with their capitals, international boundaries, surrounding countries and. Kernel Facebook Messenger New Version 2012 Rar Rar. The Bangladesh Bank robbery, also known colloquially as the Bangladesh Bank heist, took place in February 2016, when instructions to steal US951 million from. The DVB T Standard is published as EN 3. Framing structure, channel coding and modulation for digital terrestrial television. This is available from the ETSI website, as is ETSI TS 1. Specification for the use of Video and Audio Coding in Broadcasting Applications based on the MPEG 2 Transport Stream, which gives details of the DVB use of source coding methods for MPEG 2 and, more recently, H. MPEG 4 AVC as well as audio encoding systems. Many countries that have adopted DVB T have published standards for their implementation. These include the D book in the UK, the Italian DGTVi,2 the ETSI E Book and the Nordic countries and Ireland Nor. Dig. DVB T has been further developed into newer standards such as DVB H Handheld, which was a commercial failure and is no longer in operation, and DVB T2, which was initially finalised in August 2. DVB T as a digital transmission delivers data in a series of discrete blocks at the symbol rate. DVB T is a COFDM transmission technique which includes the use of a Guard Interval. It allows the receiver to cope with strong multipath situations. Within a geographical area, DVB T also allows single frequency network SFN operation, where two or more transmitters carrying the same data operate on the same frequency. In such cases the signals from each transmitter in the SFN needs to be accurately time aligned, which is done by sync information in the stream and timing at each transmitter referenced to GPS. The length of the Guard Interval can be chosen. It is a trade off between data rate and SFN capability. The longer the guard interval the larger is the potential SFN area without creating intersymbol interference ISI. It is possible to operate SFNs which do not fulfill the guard interval condition if the self interference is properly planned and monitored. Technical description of a DVB T transmitteredit. Scheme of a DVB T transmission system. With reference to the figure, a short description of the signal processing blocks follows. Source coding and MPEG 2 multiplexing MUXCompressed video, compressed audio, and data streams are multiplexed into MPEG program streams MPEG PSs. One or more MPEG PSs are joined together into an MPEG transport stream MPEG TS this is the basic digital stream which is being transmitted and received by TV sets or home Set Top Boxes STB. Allowed bitrates for the transported data depend on a number of coding and modulation parameters it can range from about 5 to about 3. Mbits see the bottom figure for a complete listing. Splitter. Two different MPEG TSs can be transmitted at the same time, using a technique called Hierarchical Transmission. It may be used to transmit, for example a standard definition SDTV signal and a high definition HDTV signal on the same carrier. Generally, the SDTV signal is more robust than the HDTV one. At the receiver, depending on the quality of the received signal, the STB may be able to decode the HDTV stream or, if signal strength lacks, it can switch to the SDTV one in this way, all receivers that are in proximity of the transmission site can lock the HDTV signal, whereas all the other ones, even the farthest, may still be able to receive and decode an SDTV signal. MUX adaptation and energy dispersal. The MPEG TS is identified as a sequence of data packets, of fixed length 1. With a technique called energy dispersal, the byte sequence is decorrelated. External encoder. A first level of error correction is applied to the transmitted data, using a non binary block code, a Reed Solomon RS 2. External interleaver. Convolutional interleaving is used to rearrange the transmitted data sequence, in such a way that it becomes more rugged to long sequences of errors. Internal encoder. A second level of error correction is given by a punctured convolutional code, which is often denoted in STBs menus as FEC Forward error correction. There are five valid coding rates 12, 23, 34, 56, and 78. Internal interleaver. Data sequence is rearranged again, aiming to reduce the influence of burst errors. This time, a block interleaving technique is adopted, with a pseudo random assignment scheme this is really done by two separate interleaving processes, one operating on bits and another one operating on groups of bits. Mapper. The digital bit sequence is mapped into a base band modulated sequence of complex symbols. There are three valid modulation schemes QPSK, 1. QAM, 6. 4 QAM. Frame adaptationthe complex symbols are grouped in blocks of constant length 1. A frame is generated, 6. Pilot and TPS signals. In order to simplify the reception of the signal being transmitted on the terrestrial radio channel, additional signals are inserted in each block. Pilot signals are used during the synchronization and equalization phase, while TPS signals Transmission Parameters Signalling send the parameters of the transmitted signal and to unequivocally identify the transmission cell. The receiver must be able to synchronize, equalize, and decode the signal to gain access to the information held by the TPS pilots. Thus, the receiver must know this information beforehand, and the TPS data is only used in special cases, such as changes in the parameters, resynchronizations, etc. Spectrum of a DVB T signal in 8k mode note the flat top characteristicsOFDM Modulation. The sequence of blocks is modulated according to the OFDM technique, using 1. Increasing the number of carriers does not modify the payload bit rate, which remains constant. Guard interval insertionto decrease receiver complexity, every OFDM block is extended, copying in front of it its own end cyclic prefix. The width of such guard interval can be 13. Cyclic prefix is required to operate single frequency networks, where there may exist an ineliminable interference coming from several sites transmitting the same program on the same carrier frequency. DAC and front end. The digital signal is transformed into an analogue signal, with a digital to analog converter DAC, and then modulated to radio frequency VHF, UHF by the RF front end.
DVB T Wikipedia. DVB T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting Terrestrial it is the DVB European based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1. UK in 1. 99. 8. 1 This system transmits compresseddigital audio, digital video and other data in an MPEG transport stream, using coded orthogonal frequency division multiplexing COFDM or OFDM modulation. It is also the format widely used worldwide including North America for Electronic News Gathering for transmission of video and audio from a mobile newsgathering vehicle to a central receive point. Rather than carrying one data carrier on a single radio frequency RF channel, COFDM works by splitting the digital data stream into a large number of slower digital streams, each of which digitally modulates a set of closely spaced adjacent sub carrier frequencies. In the case of DVB T, there are two choices for the number of carriers known as 2. K mode or 8. K mode. These are actually 1,7. Hz or 1 k. Hz apart. DVB T offers three different modulation schemes QPSK, 1. QAM, 6. 4QAM. DVB T has been adopted or proposed for digital television broadcasting by many countries see map, using mainly VHF 7 MHz and UHF 8 MHz channels whereas Taiwan, Colombia, Panama and Trinidad and Tobago use 6 MHz channels. Examples include the UKs Freeview. Map of India and Bangladesh showing the geographical location of Bangladesh and India along with their capitals, international boundaries, surrounding countries and. Kernel Facebook Messenger New Version 2012 Rar Rar. The Bangladesh Bank robbery, also known colloquially as the Bangladesh Bank heist, took place in February 2016, when instructions to steal US951 million from. The DVB T Standard is published as EN 3. Framing structure, channel coding and modulation for digital terrestrial television. This is available from the ETSI website, as is ETSI TS 1. Specification for the use of Video and Audio Coding in Broadcasting Applications based on the MPEG 2 Transport Stream, which gives details of the DVB use of source coding methods for MPEG 2 and, more recently, H. MPEG 4 AVC as well as audio encoding systems. Many countries that have adopted DVB T have published standards for their implementation. These include the D book in the UK, the Italian DGTVi,2 the ETSI E Book and the Nordic countries and Ireland Nor. Dig. DVB T has been further developed into newer standards such as DVB H Handheld, which was a commercial failure and is no longer in operation, and DVB T2, which was initially finalised in August 2. DVB T as a digital transmission delivers data in a series of discrete blocks at the symbol rate. DVB T is a COFDM transmission technique which includes the use of a Guard Interval. It allows the receiver to cope with strong multipath situations. Within a geographical area, DVB T also allows single frequency network SFN operation, where two or more transmitters carrying the same data operate on the same frequency. In such cases the signals from each transmitter in the SFN needs to be accurately time aligned, which is done by sync information in the stream and timing at each transmitter referenced to GPS. The length of the Guard Interval can be chosen. It is a trade off between data rate and SFN capability. The longer the guard interval the larger is the potential SFN area without creating intersymbol interference ISI. It is possible to operate SFNs which do not fulfill the guard interval condition if the self interference is properly planned and monitored. Technical description of a DVB T transmitteredit. Scheme of a DVB T transmission system. With reference to the figure, a short description of the signal processing blocks follows. Source coding and MPEG 2 multiplexing MUXCompressed video, compressed audio, and data streams are multiplexed into MPEG program streams MPEG PSs. One or more MPEG PSs are joined together into an MPEG transport stream MPEG TS this is the basic digital stream which is being transmitted and received by TV sets or home Set Top Boxes STB. Allowed bitrates for the transported data depend on a number of coding and modulation parameters it can range from about 5 to about 3. Mbits see the bottom figure for a complete listing. Splitter. Two different MPEG TSs can be transmitted at the same time, using a technique called Hierarchical Transmission. It may be used to transmit, for example a standard definition SDTV signal and a high definition HDTV signal on the same carrier. Generally, the SDTV signal is more robust than the HDTV one. At the receiver, depending on the quality of the received signal, the STB may be able to decode the HDTV stream or, if signal strength lacks, it can switch to the SDTV one in this way, all receivers that are in proximity of the transmission site can lock the HDTV signal, whereas all the other ones, even the farthest, may still be able to receive and decode an SDTV signal. MUX adaptation and energy dispersal. The MPEG TS is identified as a sequence of data packets, of fixed length 1. With a technique called energy dispersal, the byte sequence is decorrelated. External encoder. A first level of error correction is applied to the transmitted data, using a non binary block code, a Reed Solomon RS 2. External interleaver. Convolutional interleaving is used to rearrange the transmitted data sequence, in such a way that it becomes more rugged to long sequences of errors. Internal encoder. A second level of error correction is given by a punctured convolutional code, which is often denoted in STBs menus as FEC Forward error correction. There are five valid coding rates 12, 23, 34, 56, and 78. Internal interleaver. Data sequence is rearranged again, aiming to reduce the influence of burst errors. This time, a block interleaving technique is adopted, with a pseudo random assignment scheme this is really done by two separate interleaving processes, one operating on bits and another one operating on groups of bits. Mapper. The digital bit sequence is mapped into a base band modulated sequence of complex symbols. There are three valid modulation schemes QPSK, 1. QAM, 6. 4 QAM. Frame adaptationthe complex symbols are grouped in blocks of constant length 1. A frame is generated, 6. Pilot and TPS signals. In order to simplify the reception of the signal being transmitted on the terrestrial radio channel, additional signals are inserted in each block. Pilot signals are used during the synchronization and equalization phase, while TPS signals Transmission Parameters Signalling send the parameters of the transmitted signal and to unequivocally identify the transmission cell. The receiver must be able to synchronize, equalize, and decode the signal to gain access to the information held by the TPS pilots. Thus, the receiver must know this information beforehand, and the TPS data is only used in special cases, such as changes in the parameters, resynchronizations, etc. Spectrum of a DVB T signal in 8k mode note the flat top characteristicsOFDM Modulation. The sequence of blocks is modulated according to the OFDM technique, using 1. Increasing the number of carriers does not modify the payload bit rate, which remains constant. Guard interval insertionto decrease receiver complexity, every OFDM block is extended, copying in front of it its own end cyclic prefix. The width of such guard interval can be 13. Cyclic prefix is required to operate single frequency networks, where there may exist an ineliminable interference coming from several sites transmitting the same program on the same carrier frequency. DAC and front end. The digital signal is transformed into an analogue signal, with a digital to analog converter DAC, and then modulated to radio frequency VHF, UHF by the RF front end.